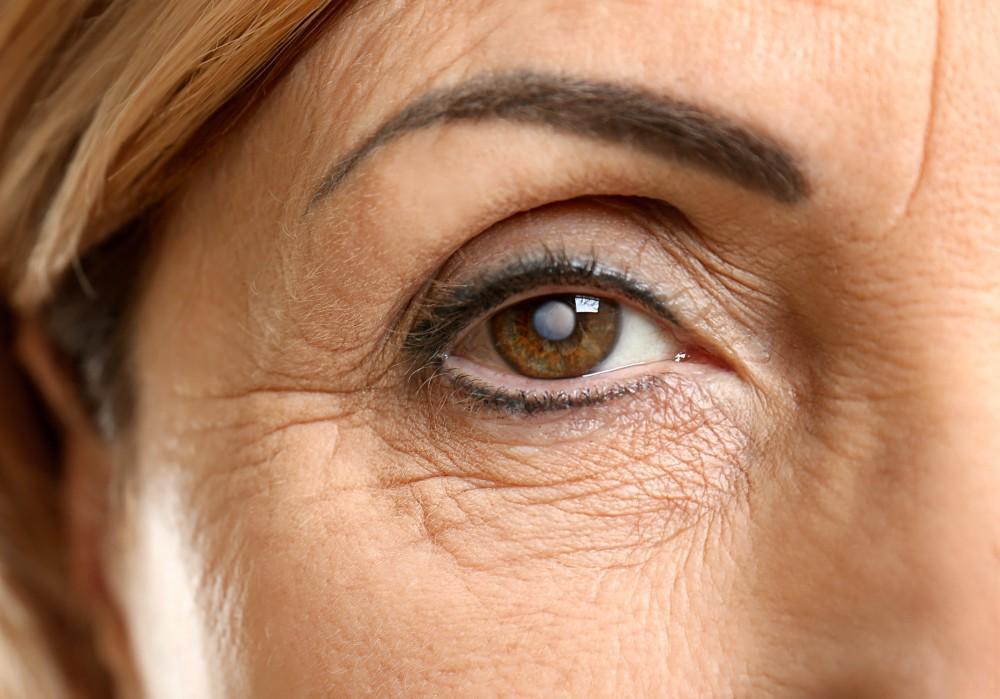
4 Telltale Signs of Cataracts
When your eyes are healthy and young, the lens that focuses light from the world...



Our team of Women’s Health experts are dedicated to providing you exceptional services including obstetrics, gynecology, mammography, ultrasounds, medical aesthetics, birth control, cancer screenings and treatment. Our services are available at 9 locations throughout Central Florida for your convenience.
We have been family trusted since 2001 and are ready to continue providing excellent patient care for generations to come.
Both exams in the same visit for our patient’s convenience.
More energy, more focus, more you.

Routine mammograms are the best way to find breast cancer early when it’s most treatable. The expert OB/GYN team at...



Our team of healthcare experts represents a diverse blend of professionals from various cultures and languages. Each provider brings specialized experience in mammography, cancer care, obstetrics, gynecology, and advanced in-office treatments. For over 23 years, we have proudly cared for the women of Central Florida and remain committed to serving future generations with the same dedication and compassion.


The Women's Center provides comprehensive care covering obstetrics, birth control, ultrasounds, gynecology, cancer screenings and treatment, medical aesthetics, and mammography. The practice also offers many procedures and minimally invasive surgeries in-office.

When your eyes are healthy and young, the lens that focuses light from the world...
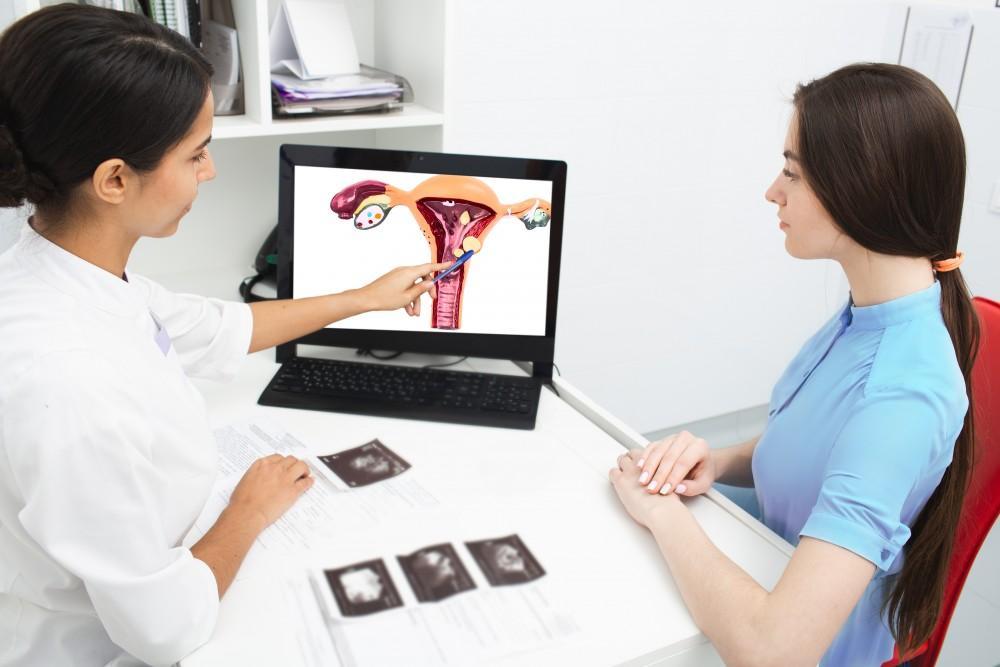
About 1 in 10 women has ovarian cysts. These small growths form on your ovaries,...
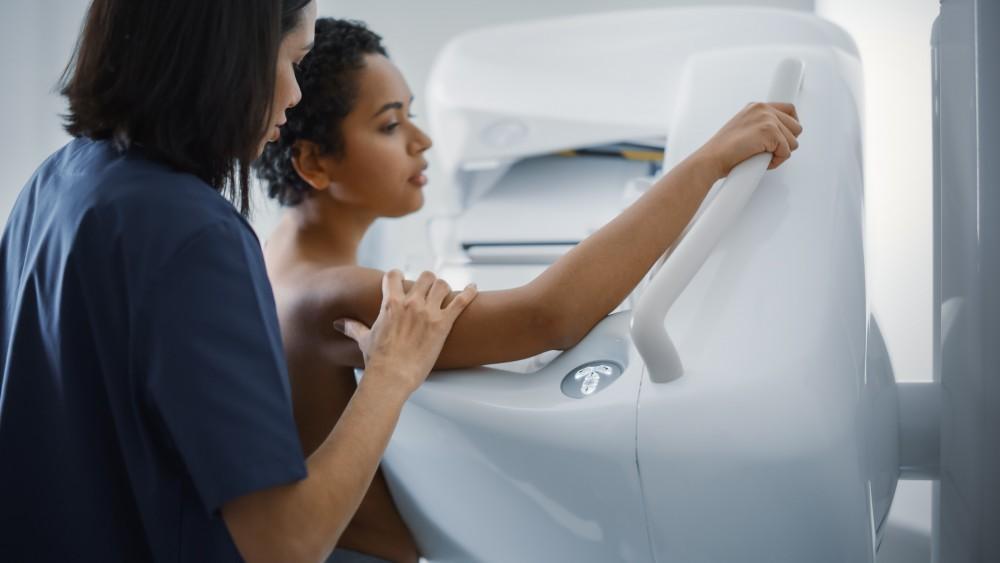

A mammogram is an X-ray of your breasts. It’s the best way to identify early...
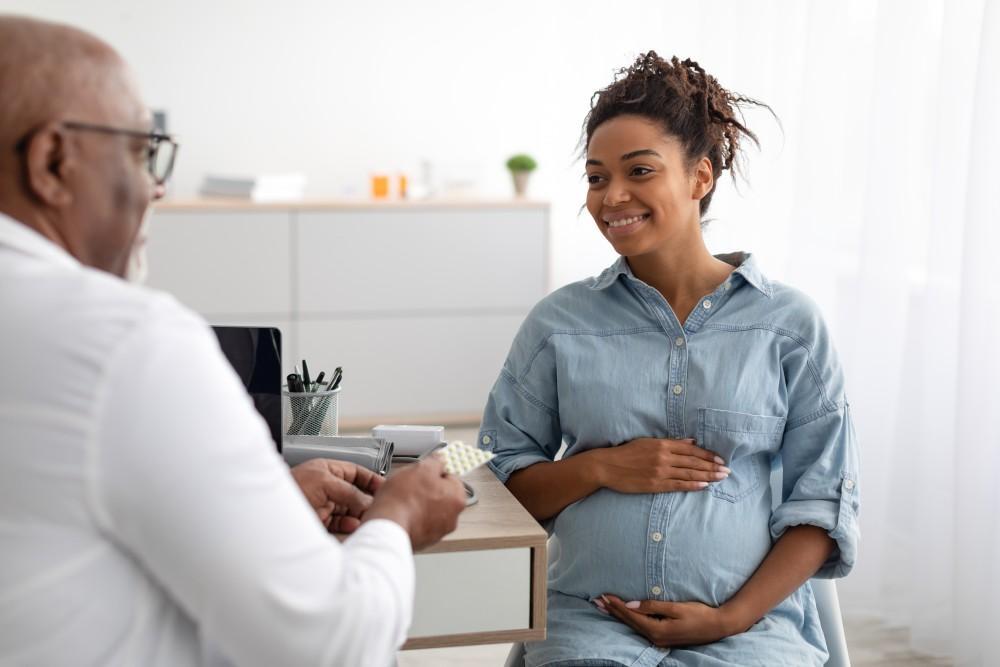

Pregnancy is a remarkable journey filled with anticipation, joy, and a lot of...
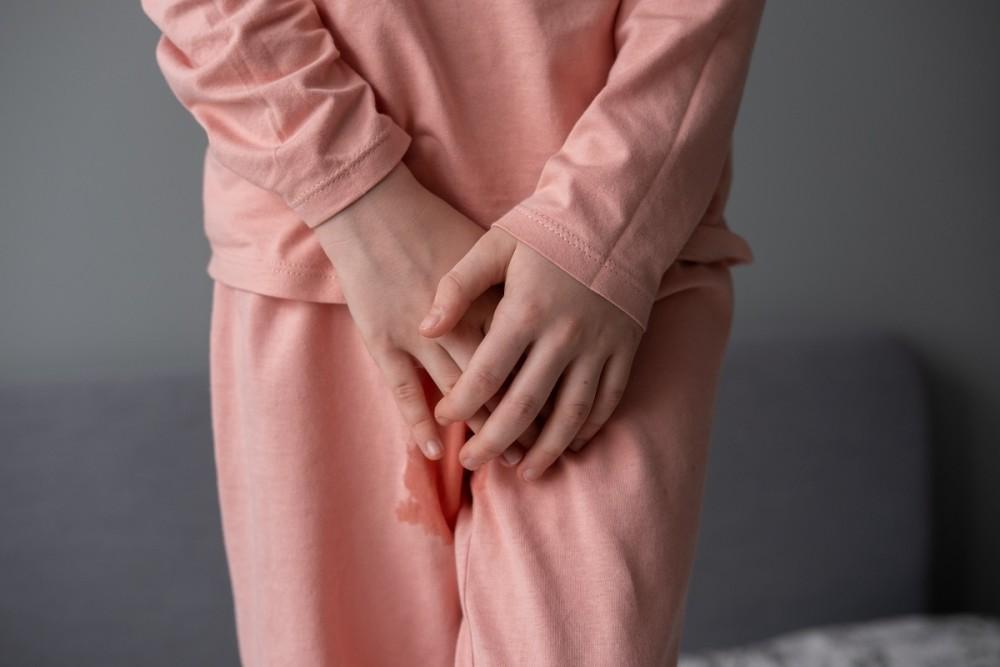

Welcoming a baby into the world is a beautiful experience. But all too often, the joys of motherhood...
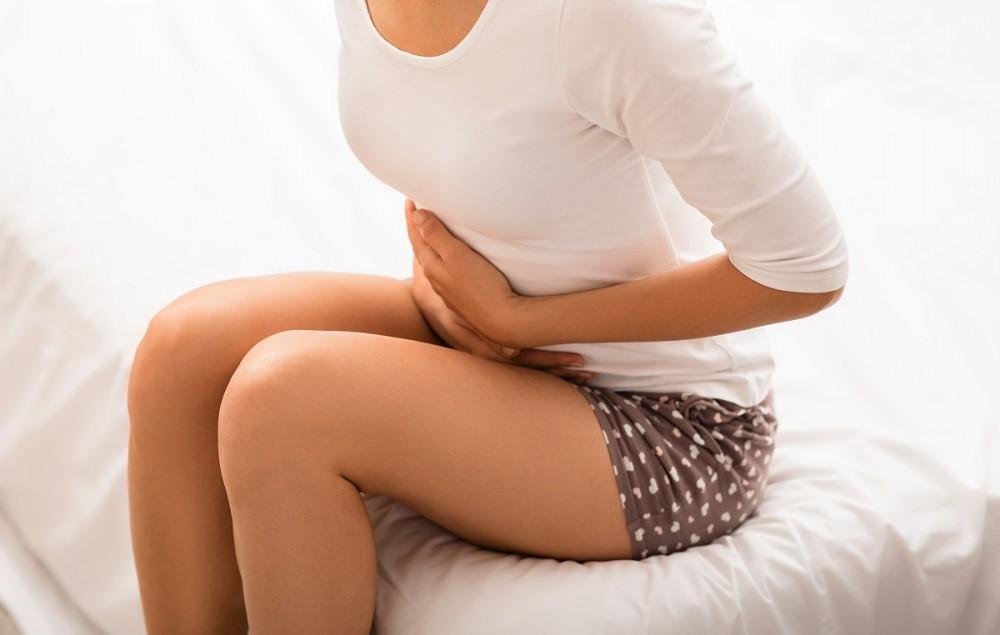

Your body experiences dramatic change during pregnancy and childbirth — and the journey continues into the postpartum period,...